
Tennis is a racquet sport that can be played individually against
a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles).
Each player uses a racquet that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball
covered with felt over or around a net and into the opponent's court. The
object of the game is to play the ball in such a way that the opponent is not
able to play a good return. The opponent who is unable to return the ball will
not gain a point, while the opposite opponent will.
Tennis is an Olympic sport and is
played at all levels of society and at all ages. The sport can be played by
anyone who can hold a racquet, including wheelchair users. The modern game of
tennis originated in Birmingham, England, in the late 19th century as "lawn
tennis". It had close connections both to various field
("lawn") games such as croquet and bowls as well as to the older
racquet sport of real tennis. During most of the 19th-century in fact,
the term "tennis" referred to real tennis, not lawn tennis: for
example, in Disraeli's novel Sybil (1845), Lord Eugene De Vere announces
that he will "go down to Hampton Court and play tennis."
The rules of tennis have changed
little since the 1890s. Two exceptions are that from 1908 to 1961 the server
had to keep one foot on the ground at all times, and the adoption of the tie-break
in the 1970s. A recent addition to professional tennis has been the adoption of
electronic review technology coupled with a point challenge system, which
allows a player to contest the line call of a point.
Tennis is played by millions of recreational
players and is also a popular worldwide spectator sport. The four Grand Slam
tournaments (also referred to as the "Majors") are especially
popular: the Australian Open played on hard courts, the French Open played on
red clay courts, Wimbledon played on grass courts, and the US Open played also
on hard courts.
History
Predecessors

Jeu de paume in the 17th century
Historians believe that the game's
ancient origin lay in 12th century northern France, where a ball was struck
with the palm of the hand. Louis X of France was a keen player of jeu de paume
("game of the palm"), which evolved into real tennis, and became
notable as the first person to construct indoor tennis courts in the modern
style. Louis was unhappy with playing tennis out of doors and accordingly had
indoor, enclosed courts made in Paris "around the end of the 13th
century". In due course this design spread across royal palaces all over
Europe. In June 1316 at Vincennes, Val-de-Marne and following a particularly
exhausting game, Louis drank a large quantity of cooled wine and subsequently
died of either pneumonia or pleurisy, although there was also suspicion of
poisoning. Because of the contemporary accounts of his death, Louis X is
history's first tennis player known by name. Another of the early
enthusiasts of the game was King Charles V of France, who had a court set up at
the Louvre Palace.
It wasn't until the 16th century
that racquets came into use, and the game began to be called
"tennis", from the Old French term tenez, which can be
translated as "hold!", "receive!" or "take!", an interjection
used as a call from the server to his opponent. It was popular in England and
France, although the game was only played indoors where the ball could be hit
off the wall. Henry VIII of England was a big fan of this game, which is now
known as real tennis. During the 18th century and early 19th century, as real
tennis declined, new racquet sports emerged in England.
Further, the patenting of the first lawn
mower in 1830, in Britain, is strongly believed to have been the catalyst,
world-wide, for the preparation of modern-style grass courts, sporting ovals,
playing fields, pitches, greens, etc. This in turn led to the codification of
modern rules for many sports, including lawn tennis, most football codes, lawn
bowls and others.
Origins
of the modern game

Augurio Perera's house in Edgbaston,
Birmingham, where he and Harry Gem first played the modern game of lawn tennis
Between 1859 and 1865 Harry Gem and
his friend Augurio Perera developed a game that combined elements of racquets
and the Basque ball game pelota, which they played on Perera's croquet lawn in Birmingham,
England, United Kingdom. In 1872, along with two local doctors, they founded
the world's first tennis club in Leamington Spa.
In December 1873, British army
officer Major Walter Clopton Wingfield designed and patented a similar
game – which he called sphairistikè (Greek: σφαιριστική, meaning "ball-playing"), and was soon known
simply as "sticky" – for the amusement of guests at a garden
party on his friend's estate of Nantclwyd Hall, in Llanelidan, Wales. According
to R. D. C. Evans, turfgrass agronomist, "Sports historians all agree that
[Wingfield] deserves much of the credit for the development of modern
tennis." According to Honor Godfrey, museum curator at Wimbledon,
Wingfield "popularized this game enormously. He produced a boxed set which
included a net, poles, racquets, balls for playing the game -- and most
importantly you had his rules. He was absolutely terrific at marketing and he
sent his game all over the world. He had very good connections with the clergy,
the law profession, and the aristocracy and he sent thousands of sets out in
the first year or so, in 1874." The world's oldest tennis tournament, the Wimbledon
Championships, were first played in London in 1877. The first Championships
culminated a significant debate on how to standardize the rules.
In the U.S. in 1874 Mary Ewing
Outerbridge, a young socialite, returned from Bermuda with a sphairistikè set.
She became fascinated by the game of tennis after watching British army
officers play. She laid out a tennis court at the Staten Island Cricket Club at
Camp Washington, Tompkinsville, Staten Island, New York. The first American
National championship was played there in September 1880. An Englishman named
O.E Woodhouse won the singles title, and a silver cup worth $100, by defeating
Canadian I. F. Hellmuth. There was also a doubles match which was won by a
local pair. There were different rules at each club. The ball in Boston was
larger than the one normally used in New York. On 21 May 1881, the United
States National Lawn Tennis Association (now the United States Tennis Association)
was formed to standardize the rules and organize competitions. The U.S.
National Men's Singles Championship, now the US Open, was first held in 1881 at
the Newport Casino, Newport, Rhode Island. The U.S. National Women's Singles
Championships were first held in 1887 in Philadelphia.

Lawn tennis in Canada, ca. 1900
Tennis also became popular in
France, where the French Championships dates to 1891 although until 1925 it was
open only to tennis players who were members of French clubs. Thus, Wimbledon,
the US Open, the French Open, and the Australian Open (dating to 1905) became
and have remained the most prestigious events in tennis. Together these four
events are called the Majors or Slams (a term borrowed from bridge
rather than baseball).
The comprehensive rules promulgated
in 1924 by the International Lawn Tennis Federation, now known as the International
Tennis Federation (ITF), have remained largely stable in the ensuing eighty
years, the one major change being the addition of the tie-break system
designed by James Van Alen. That same year, tennis withdrew from the Olympics
after the 1924 Games but returned 60 years later as a 21-and-under
demonstration event in 1984. This reinstatement was credited by the efforts by
the then ITF President Philippe Chatrier, ITF General Secretary David Gray and
ITF Vice President Pablo Llorens, and support from IOC President Juan Antonio
Samaranch. The success of the event was overwhelming and the IOC decided to
reintroduce tennis as a full medal sport at Seoul in 1988.

International Tennis Hall of Fame at
the Newport Casino
The Davis Cup, an annual competition
between men's national teams, dates to 1900. The analogous competition for
women's national teams, the Fed Cup, was founded as the Federation Cup in 1963
to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the founding of the ITF.
In 1926, promoter C. C. Pyle
established the first professional tennis tour with a group of American and
French tennis players playing exhibition matches to paying audiences. The most
notable of these early professionals were the American Vinnie Richards and the
Frenchwoman Suzanne Lenglen. Once a player turned pro he or she could
not compete in the major (amateur) tournaments. This resulted in a schism
between the amateur and pro tennis ranks that would last until the advent of
the Open Era.
In 1968, commercial pressures and
rumors of some amateurs taking money under the table led to the abandonment of
this distinction, inaugurating the open era, in which all players could compete
in all tournaments, and top players were able to make their living from tennis.
With the beginning of the open era, the establishment of an international
professional tennis circuit, and revenues from the sale of television rights,
tennis's popularity has spread worldwide, and the sport has shed its
middle-class English-speaking image (although it is acknowledged that this
stereotype still exists).
In 1954, Van Alen founded the International
Tennis Hall of Fame, a non-profit museum in Newport, Rhode Island. The building
contains a large collection of tennis memorabilia as well as a hall of fame
honoring prominent members and tennis players from all over the world. Each
year, a grass-court tournament and an induction ceremony honoring new Hall of
Fame members are hosted on its grounds.
Equipment
Part of the appeal of tennis stems
from the simplicity of equipment required for play. Beginners need only a racquet
and balls.
Racquets
The components of a tennis racquet
include a handle, known as the grip, connected to a neck which joins a roughly
elliptical frame that holds a matrix of tightly pulled strings. For the first
100 years of the modern game, racquets were of wood and of standard size, and
strings were of animal gut. Laminated wood construction yielded more strength
in racquets used through most of the 20th century until first metal and then
composites of carbon graphite, ceramics, and lighter metals such as titanium
were introduced. These stronger materials enabled the production of over-sized
racquets that yielded yet more power. Meanwhile technology led to the use of
synthetic strings that match the feel of gut yet with added durability.
Under modern rules of tennis, the
racquets must adhere to the following guidelines;
- The hitting area, composed of the strings, must be flat and generally uniform.
- The frame of the hitting area may not be more than 29 inches in length and 12.5 inches in width.
- The entire racquet must be of a fixed shape, size, weight, and weight distribution. There may not be any energy source built into the racquets.
- The racquets must not provide any kind of communication, instruction or advice to the player during the match.
The rules regarding racquets have
changed over time, as material and engineering advances have been made. For
example, the maximum length of the frame had been 32 inches until 1997,
when it was shortened to 29 inches.
A tennis racquet and balls.
 Many companies manufacture and
distribute tennis racquets. Wilson, Head and Babolat are some of the more
commonly used brands; however, many more companies exist. The same companies
sponsor players to use these racquets in the hopes that the company name will
become more well known by the public.
Many companies manufacture and
distribute tennis racquets. Wilson, Head and Babolat are some of the more
commonly used brands; however, many more companies exist. The same companies
sponsor players to use these racquets in the hopes that the company name will
become more well known by the public.
Balls
Tennis balls have come a long way
from being made of cloth strips stitched together with thread. Tennis balls are
made of hollow rubber with a felt coating. Traditionally white, the predominant
color was gradually changed to optic yellow in the latter part of the 20th
century to allow for improved visibility. Tennis balls must conform to certain
criteria for size, weight, deformation, and bounce to be approved for
regulation play. The International Tennis Federation (ITF) defines the official
diameter as 65.41-68.58 mm (2.575-2.700 inches). Balls must weigh
between 56.0 and 59.4 grams (1.975-2.095 ounces). Tennis balls were
traditionally manufactured in the United States and Europe. Although the
process of producing the balls has remained virtually unchanged for the past
100 years, the majority of manufacturing now takes place in the Far East. The
relocation is due to cheaper labour costs and materials in the region.
Miscellaneous
Advanced players improve their
performance through a number of accoutrements. Vibration dampers may be
interlaced in the proximal part of the string array for improved feel. Racquet
handles may be customized with absorbent or rubber-like materials to improve
the players' grip. Players often use sweat bands on their wrists to keep their
hands dry as well. Finally, although the game can be played in a variety of
shoes, specialized tennis shoes have wide, flat soles for stability and a
built-up front structure to avoid excess wear.
Manner
of play
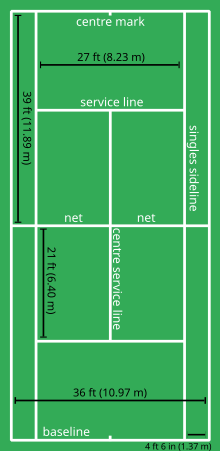
The dimensions of a tennis court

Two players before a serve
Court
Tennis is played on a rectangular,
flat surface, usually grass, clay, or a hardcourt of concrete, asphalt, or
acrylic; occasionally carpet is used for indoor play. The court is 78 feet
(23.77 m) long, and 27 feet (8.23 m) wide for singles matches
and 36 ft (10.97 m) for doubles matches.Additional clear space around
the court is required in order for players to reach overrun balls. A net is
stretched across the full width of the court, parallel with the baselines,
dividing it into two equal ends. It is held up by either a metal cable or cord
that can be no more than 0.8 cm (1/3 inch).The net is 3 feet
6 inches (1.067 m) high at the posts and 3 feet (0.914 m)
high in the center. The net posts are 3 feet (0.914 m) outside the
doubles court on each side or, for a singles net, 3 feet (0.914 m)
outside the singles court on each side. There are grass courts, hard courts,
clay courts and other surfaces as well.
The modern tennis court owes its
design to Major Walter Clopton Wingfield who, in 1873, patented a court much
the same as the current one for his stické tennis (sphairistike). This template
was modified in 1875 to the court design that exists today, with markings
similar to Wingfield's version, but with the hourglass shape of his court
changed to a rectangle.
Lines
The lines that delineate the width
of the court are called the baseline (farthest back) and the service line
(middle of the court). The short mark in the center of each baseline is
referred to as either the hash mark or the center mark. The outermost lines
that make up the length are called the doubles sidelines. These are the
boundaries used when doubles is being played. The lines to the inside of the
doubles sidelines are the singles sidelines and are used as boundaries in
singles play. The area between a doubles sideline and the nearest singles
sideline is called the doubles alley, which is considered playable in doubles
play. The line that runs across the center of a player's side of the court is
called the service line because the serve must be delivered into the area
between the service line and the net on the receiving side. Despite its name,
this is not where a player legally stands when making a serve.
The line dividing the service line
in two is called the center line or center service line. The boxes this center
line creates are called the service boxes; depending on a player's position, he
or she will have to hit the ball into one of these when serving. A ball is out
only if none of it has hit the line or the area inside the lines upon its first
bounce. All the lines are required to be between 1 and 2 inches (51 mm) in
width. The baseline can be up to 4 inches (100 mm) wide.
Play
of a single point
Main article: Point (tennis)
The players (or teams) start on
opposite sides of the net. One player is designated the server, and the
opposing player is the receiver. The choice to be server or receiver in
the first game and the choice of ends is decided by a toss before the warm-up
starts. Service alternates game by game between the two players (or teams.) For
each point, the server starts behind the baseline, between the center mark and
the sideline. The receiver may start anywhere on their side of the net. When
the receiver is ready, the server will serve, although the receiver must play
to the pace of the server.
In a legal service, the ball travels
over the net (without touching it) and into the diagonally opposite service
box. If the ball hits the net but lands in the service box, this is a let
or net service, which is void, and the server retakes that serve. The
player can serve any number of let services in a point and they are always
treated as voids and not as faults. A fault is a serve that falls long or wide
of the service box, or does not clear the net. There is also a "foot
fault", which occurs when a player's foot touches the baseline or an extension
of the center mark before the ball is hit. If the second service is also a
fault, the server double faults, and the receiver wins the point.
However, if the serve is in, it is considered a legal service.
A legal service starts a rally,
in which the players alternate hitting the ball across the net. A legal return
consists of the player or team hitting the ball before it has bounced twice or
hit any fixtures except the net, provided that it still falls in the server's
court. A player or team cannot hit the ball twice in a row. The ball must
travel past the net into the other players' court. A ball that hits the net
during a rally is still considered a legal return. The first player or team to
fail to make a legal return loses the point. The server then moves to the other
side of the service line at the start of a new point.
Scoring
"Break point" redirects
here. For software term, see Breakpoint.
Game,
Set, Match
Game
A game consists of a sequence of points
played with the same player serving. A game is won by the first player to have
won at least four points in total and at least two points more than the
opponent. The running score of each game is described in a manner peculiar to
tennis: scores from zero to three points are described as "love",
"fifteen", "thirty", and "forty"
respectively. If at least three points have been scored by each player, making
the player's scores equal at forty apiece, the score is not called out as
"forty-forty", but rather as "deuce". If at least
three points have been scored by each side and a player has one more point than
his opponent, the score of the game is "advantage" for the
player in the lead. During informal games, "advantage" can
also be called "ad in" or "van in" when the
serving player is ahead, and "ad out" or "van out"
when the receiving player is ahead.

The scoreboard of a match between Andy
Roddick and Cyril Saulnier.
The score of a tennis game during
play is always read with the serving player's score first. In tournament play,
the chair umpire calls the point count (e.g., "fifteen-love")
after each point. At the end of a game, the chair umpire also announces the
winner of the game and the overall score.
Set
A set consists of a sequence of
games played with service alternating between games, ending when the count of
games won meets certain criteria. Typically, a player wins a set by winning at
least six games and at least two games more than the opponent. If one player
has won six games and the opponent five, an additional game is played. If the
leading player wins that game, the player wins the set 7–5. If the trailing
player wins the game, a tie-break is played. A tie-break, played under a
separate set of rules, allows one player to win one more game and thus the set,
to give a final set score of 7–6. A "love" set means that the loser
of the set won zero games, colloquially termed a 'jam donut' in the USA. In
tournament play, the chair umpire announces the winner of the set and the
overall score. The final score in sets is always read with the winning player's
score first, e.g. "6–2, 4–6, 6–0, 7–5".
Match
A match consists of a sequence of
sets. The outcome is determined through a best of three or five sets
system. Recreational players may agree to play any number of sets, depending
upon time availability or stamina. On the professional circuit, men play
best-of-five-set matches at all four Grand Slam tournaments, Davis Cup, and the
final of the Olympic Games and best-of-three-set matches at all other
tournaments, while women play best-of-three-set matches at all tournaments. The
first player to win two sets in a best-of-three, or three sets in a
best-of-five, wins the match. Only in the final sets of matches at the Australian
Open, the French Open, Wimbledon, the Olympic Games, Davis Cup, and Fed Cup are
tie-breaks not played. In these cases, sets are played indefinitely until one
player has a two-game lead, leaded to some remarkably long matches.
In tournament play, the chair umpire
announces the end of the match with the well-known phrase "Game, set,
match" followed by the winning person's or team's name.
Special
point terms
Game point
A game point occurs in tennis
whenever the player who is in the lead in the game needs only one more point to
win the game. The terminology is extended to sets (set point), matches (match
point), and even championships (championship point). For example, if the player
who is serving has a score of 40-love, the player has a triple game point
(triple set point, etc.) as the player has three consecutive chances to win the
game. Game points, set points, and match points are not part of official
scoring and are not announced by the chair umpire in tournament play.
Break point
A break point occurs if the
receiver, not the server, has a chance to win the game with the next point.
Break points are of particular importance because serving is generally
considered advantageous, with the server being expected to win games in which
they are serving. A receiver who has one (score of 30–40), two (score of 15–40)
or three (score of love-40) consecutive chances to win the game has break
point, double break point or triple break point,
respectively. If the receiver does, in fact, win their break point, the game is
awarded to the receiver, and the receiver is said to have converted
their break point. If the receiver fails to win their break point it is called
a failure to convert. Winning break points, and thus the game, is also
referred to as breaking serve, as the receiver has disrupted, or broken
the natural advantage of the server. If in the following game the previous
server also wins a break point it is referred to as breaking back. At
least one break of serve is required to win a set.
Rule
variations
- No ad
From 'No advantage'. Scoring method created by Jimmy Van
Alen. The first player or doubles team to win four points wins the game,
regardless of whether the player or team is ahead by two points. When the game
score reaches three points each, the receiver chooses which side of the court
(advantage court or deuce court) the service is to be delivered on the seventh
and game-deciding point. Utilized by World Team Tennis professional competition
and ITF Junior Doubles.
- Pro set
Instead of playing multiple sets, players may play one
"pro set". A pro set is first to 8 (or 10) games by a margin of two
games, instead of first to 6 games. A 12-point tie-break is usually played when
the score is 8–8 (or 10–10). These are often played with no-ad scoring.
- Match tie-break
This is sometimes played instead of a third set. A match
tie-break is played like a regular tie-break, but the winner must win ten
points instead of seven. Match tie-breaks are used in the Hopman Cup and the 2012
Olympic Games for mixed doubles, on the ATP and WTA tours for doubles and as a
player's choice in USTA league play.
Another, however informal, tennis
format is called Canadian doubles. This involves three players, with one person
playing a doubles team. The single player gets to utilize the alleys normally
reserved only for a doubles team. Conversely, the doubles team does not use the
alleys when executing a shot. The scoring is the same as a regular game. This
format is not sanctioned by any official body.
"Australian doubles",
another informal and unsanctioned form of tennis, is played with similar rules
to the Canadian doubles style, only in this version, players rotate court
position after each game. As such, each player plays doubles and singles over
the course of a match, with the singles player always serving. Scoring styles
vary, but one popular method is to assign a value of 2 points to each game,
with the server taking both points if he or she holds serve and the doubles
team each taking one if they break serve.
Wheelchair tennis can be played by
able-bodied players as well as people who require a wheelchair for mobility. An
extra bounce is permitted. This rule makes it possible to have mixed wheelchair
and able-bodied matches. It is possible for a doubles team to consist of a
wheelchair player and an able-bodied player (referred to as "one-up,
one-down"), or for a wheelchair player to play against an able-bodied
player. In such cases, the extra bounce is permitted for the wheelchair users
only.
Surface
There are five types of court
surface used in professional play. Each surface is different in the speed and
height of the bounce of the ball. The same surface plays faster indoors than
outdoors.
- Clay
Examples are red clay, used at the French Open, and green
clay (an example of which is Har-Tru and used mainly in the U.S.). Almost all
red clay courts are made not of natural clay but of crushed brick that is
packed to make the court. The crushed brick is then covered with a topping of
other crushed particles. This type of surface does not absorb water easily and
is the most common in Europe and Latin America. Clay courts normally have a
slower paced ball and a fairly true bounce with more spin.
- Hard
Examples of hardcourts are acrylic (e.g. Plexicushion used
at the Australian Open, DecoTurf used at the US Open, GreenSet used at the ATP
World Tour Finals), asphalt, and concrete. Hardcourts typically have a
faster-paced ball with a very true bounce and it is the predominant surface
type used on the professional tour.
- Grass
Grass courts usually have a faster-paced ball, and a more
erratic bounce. Grass is used at Wimbledon and until 1974 three of the four
Grand Slams (Australian Open, Wimbledon, US Open) were played on grass. In 2001
Wimbledon changed the type of grass to make the courts more durable and thus
better able to withstand the wear of the modern game. The new grass causes the
ball to bounce higher and slows it down compared to the previous grass type.
- Carpet
Any form of removable court covering, including carpeting
and artificial turf. The bounce can be higher or lower than a hard court.
Carpet surface has not been used on the ATP and WTA tour since 2009.
- Wood
Popular from the 1880s through the first half of the 20th
century, wooden surface provides a very low bounce and plays very fast. There
are no longer any professional tournaments held on a wooden surface although
some tournaments (e.g. Rotterdam Open and Open Sud de France), are played on a
wood-based court with an acrylic layer on top.
Officials

An umpire informing two players of
the rules
In most professional play and some
amateur competition, there is an officiating head judge or chair umpire
(usually referred to as the umpire), who sits in a raised chair to one side of
the court. The umpire has absolute authority to make factual determinations.
The umpire may be assisted by line judges, who determine whether the ball has
landed within the required part of the court and who also call foot faults.
There also may be a net judge who determines whether the ball has touched the
net during service. The umpire has the right to overrule a line judge or a net
judge if the umpire is sure that a clear mistake has been made
In some tournaments, line judges who
would be calling the serve, were assisted by electronic sensors that beeped to
indicate the serve was out. This system was called "Cyclops". Cyclops
has since largely been replaced by the Hawk-Eye system. In professional
tournaments using this system, players are allowed three unsuccessful appeals
per set, plus one additional appeal in the tie-break to challenge close line
calls by means of an electronic review. The US Open, Miami Masters, US Open
Series, and World Team Tennis started using this challenge system in 2006 and
the Australian Open and Wimbledon introduced the system in 2007.In clay-court
matches, such as at the French Open, a call may be questioned by reference to
the mark left by the ball's impact on the court surface.
The referee, who is usually located
off the court, is the final authority about tennis rules. When called to the
court by a player or team captain, the referee may overrule the umpire's
decision if the tennis rules were violated (question of law) but may not change
the umpire's decision on a question of fact. If, however, the referee is on the
court during play, the referee may overrule the umpire's decision (This would
only happen in Davis Cup or Fed Cup matches, not at the World Group level, when
a chair umpire from a non-neutral country is in the chair).
Ball boys and girls may be employed
to retrieve balls, pass them to the players, and hand players their towels.
They have no adjudicative role. In rare events (e.g., if they are hurt or if
they have caused a hindrance), the umpire may ask them for a statement of what
actually happened. The umpire may consider their statements when making a
decision. In some leagues, especially junior leagues, players make their own
calls, trusting each other to be honest. This is the case for many school and
university level matches. The referee or referee's assistant, however, can be
called on court at a player's request, and the referee or assistant may change
a player's call. In unofficiated matches, a ball is out only if the player
entitled to make the call is sure that the ball is out.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

No comments:
Post a Comment